How Does Blood Help Maintain Homeostasis
Homeostatic regulation homeostasis physiology cardiovascular vascular flowchart mechanisms endocrine responses circulatory circulation neural shock angiotensin decreased renin skeletal fluids Maintaining homeostasis Respiratory system and homeostasis
Homeostasis of blood glucose (a negative feedback loop) - YouTube
20.4 homeostatic regulation of the vascular system – douglas college Homeostasis- definition, types, examples, applications Homeostasis of blood glucose (a negative feedback loop)
Homeostasis glucose internal stable food glucagon pancreas insulin bloodstream expii
Body homeostasis regulation human feedback negative blood glucose system control example mechanisms stimulus positive hormone systems which biology level notWhat is homeostasis? why is it so important for our wellbeing? Homeostasis and regulation in the human body ‹ opencurriculumMaintain stable internal environment (homeostasis).
Homeostasis function feedback temperature regulation chemistry cellular homeostatic positive humans fever during coreHomeostasis (anatomy & physiology l ) Homeostasis system urinary angiotensin renin enzyme anatomy regulation osmolarity physiology figure converts pro iiHomeostasis maintained organs.

Circulatory system homeostasis
Homeostasis explained stasis homeo ppt feedback powerpoint negative stationary stable same static rate presentation change normal ex responseHomeostasis cells does maintain help communication between regulation calcium figure pediaa levels Ch103 – chapter 8: homeostasis and cellular function – chemistryGlucose homeostasis endocrine insulin glucagon effects blood control sugar levels homeostatic level regulation pancreas feedback negative hormonal example increase cells.
Homeostasis glucose environment internal glucagon pancreas bloodstream insulin expiiHomeostasis anatomy physiology feedback regulation thermoregulation mechanism effector positive endocrine diabetes studyblue explaining How does communication between cells help maintain homeostasisHomeostasis skeletal system maintaining.

Maintain stable internal environment (homeostasis)
The urinary system and homeostasis · anatomy and physiologyWhat is homeostasis? » scienceabc Feedback loop negative glucose blood homeostasisHomeostasis maintain chapter vessels.
Circulatory homeostasisHomeostasis respiratory oxygen .


Homeostasis (Anatomy & Physiology l ) | My Biology Notebook

Maintaining Homeostasis - The Skeletal System

CH103 – Chapter 8: Homeostasis and Cellular Function – Chemistry

Maintain Stable Internal Environment (Homeostasis) - Expii

20.4 Homeostatic Regulation of the Vascular System – Douglas College
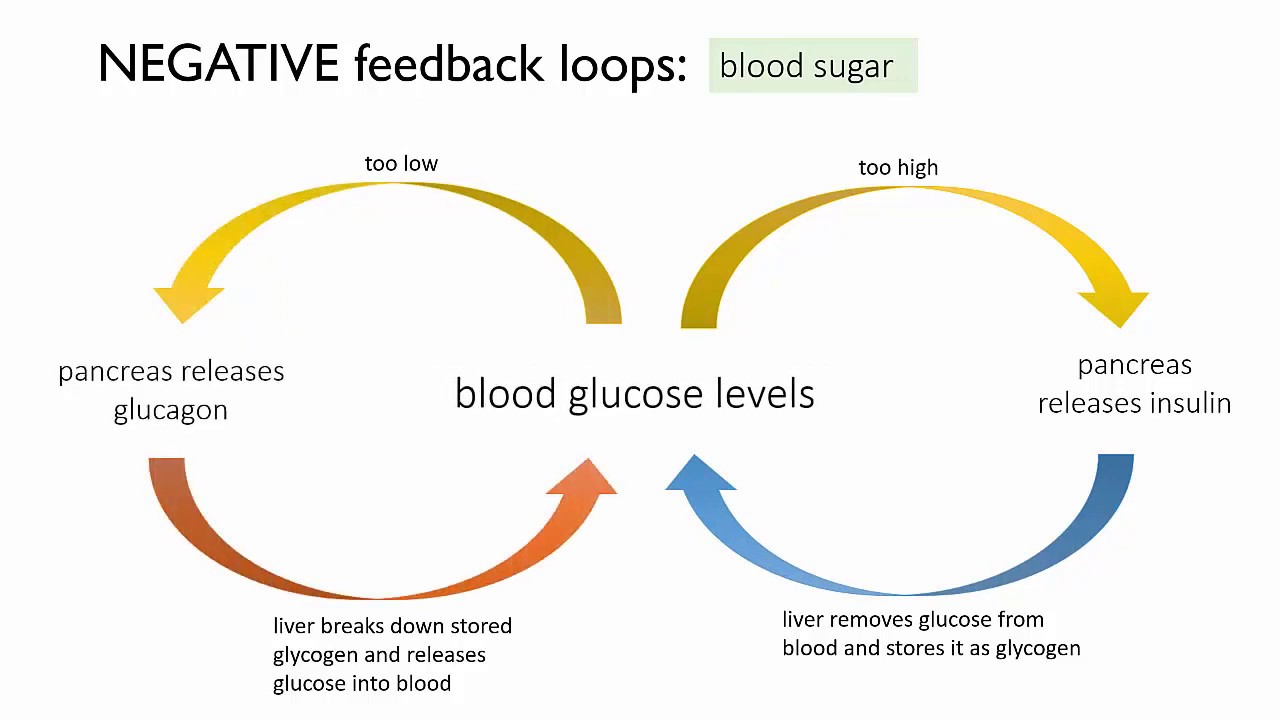
Homeostasis of blood glucose (a negative feedback loop) - YouTube

How Does Communication Between Cells Help Maintain Homeostasis - Pediaa.Com

Maintain Stable Internal Environment (Homeostasis) - Expii

What is Homeostasis? Why Is It so Important For Our Wellbeing?
